
A celestial dance between two stars around 3,000 light years away will result in an outburst so bright it could be seen by the naked eye for several days, astronomers say.
The once-in-a-lifetime explosion in the T Coronae Borealis system will give it the appearance of a new star shining brightly in the night sky, before fading away again for another 80 years.
Dr Daniel Brown, an associate professor in astronomy at Nottingham Trent University, said this type of celestial event is called a nova, where a star’s brightness increases rapidly.
He said it is not easy to predict when exactly this event will occur but it could take place any time between now and September this year.
Prof Brown said: “We are in for a treat, being granted a so-called new star in the skies.
“T Coronae Borealis is actually not a single star but a binary, so two stars orbiting each other.
“What makes this pair so special is that every so often it increases its brightness immensely to become easily visible to us.”
He said the more massive star in the pair is a white dwarf, which “can pack roughly the same mass as our Sun in a volume as large as Earth”.
Its companion, an ageing red giant, has expanded and is steadily dumping its material on to the white dwarf.
Prof Brown said: “Every 80 years or so it (the white dwarf) gathers enough material so that it ignites in a thermonuclear explosion, boosting its brightness incredibly.
“For T Coronae Borealis, the time is up for another such explosion, taking its brightness from 11mag – just about visible with binoculars in a dark sky – to a whopping 2mag – comparable to the stars in the Plough and easy to spot with the naked eye, in even light polluted skies.”
Following the outburst, T Coronae Borealis will be become the brightest star in the constellation of Corona Borealis before gradually dimming after several days.
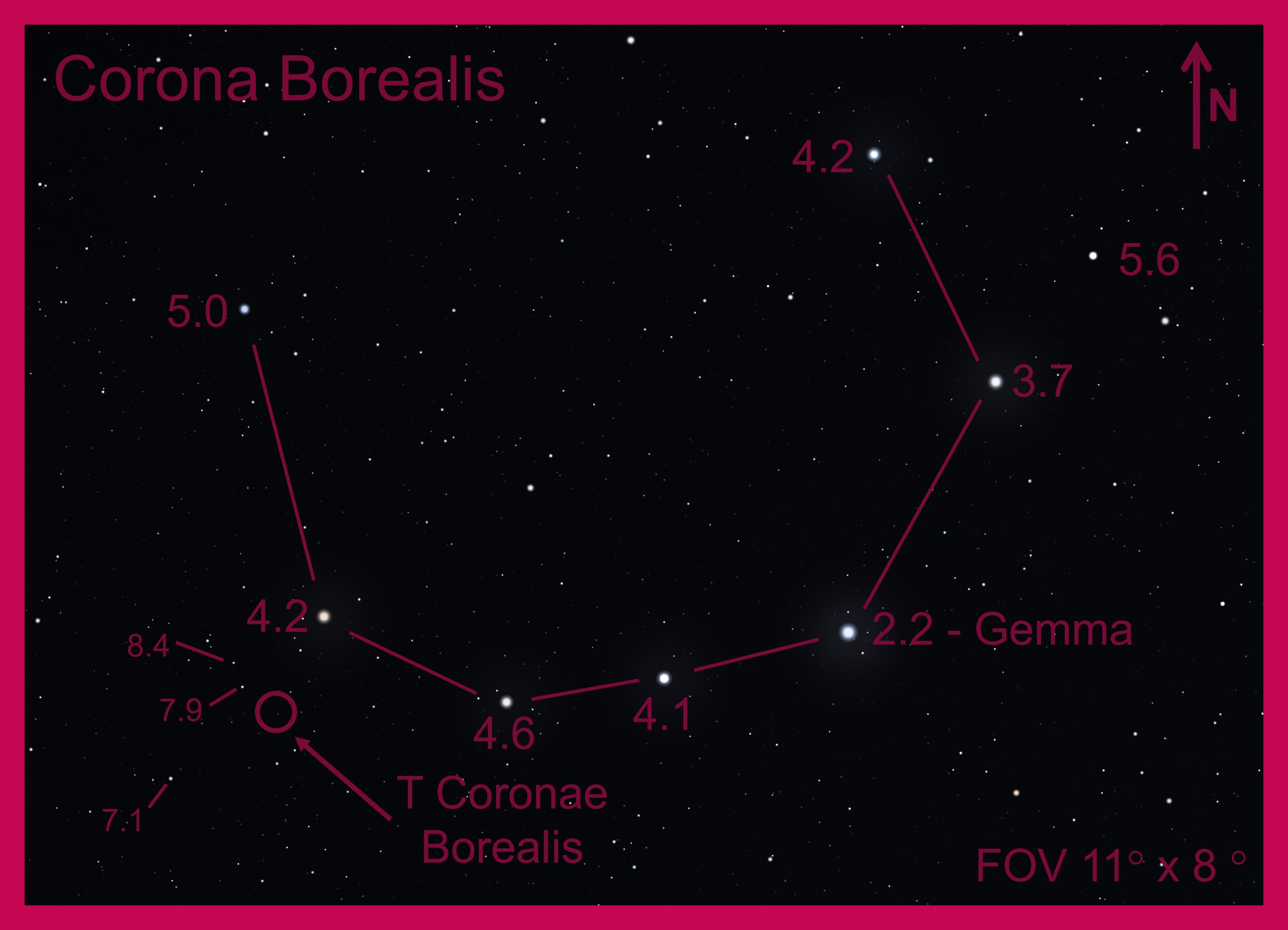
Prof Brown said the constellation can be seen in the UK, currently rising just after sunset in the North East.
He said: “It will be visible at its highest altitude in the South at 65 degrees above the horizon just after 3am, making observing easy.
“As we progress through spring, it will rise earlier and reach its highest altitude earlier as well.
“So we are in luck, as we approach the best time of the year to observe it.”
Prof Brown said the Corona Borealis constellation can be spotted by following the Plough’s handle in a curve down towards the star Arcturus, the brightest star in the constellation of Bootes.
He said: “This constellation is shaped like a kite with Arcturus at the bottom.
“Having spotted Bootes, Corona Borealis is the U-shape arc to the left of the kite.”
For those wanting to follow the brightening of T Coronae Borealis, Prof Brown advises using binoculars to become familiar with the region and the stars in Corona Borealis.
He said: “As the outbreak starts, you can start to compare its brightness against the other stars and, thereby, follow the outbreak yourself without needing any fancy cameras.”

Enjoy the convenience of having The Sunday Post delivered as a digital ePaper straight to your smartphone, tablet or computer.
Subscribe for only £5.49 a month and enjoy all the benefits of the printed paper as a digital replica.
Subscribe